시작하기 전에
heap(힙) 이란 자료구조는 우선 순위 큐를 위하여 만들어진 자료구조라고 한다. 그렇다면 우선 순위 큐란 무엇이기에 이를 위해서 자료구조 힙이 필요한 것일까?
우선 순위 큐는 말 그대로 우선 순위의 개념을 큐에 도입한 자료구조이다. 즉 데이터들이 우선순위를 가지고 있고 우선순위가 높은 데이터가 먼저 나가게 된다. 하단의 이미지를 참고하면, 우선 순위 큐와 기존의 스택,큐 자료구조와 구분이 가능할 것이다.
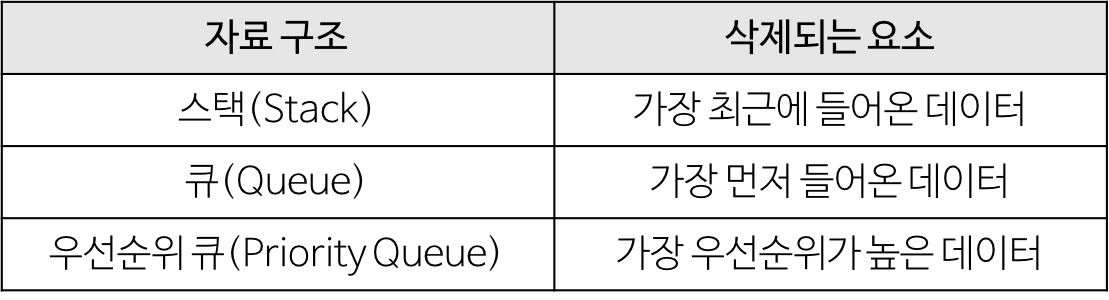
사실 우선 순위 큐를 꼭 힙으로만 구현해야 하는 것은 아니지만, 힙으로 구현 하는 것이 가장 효율적이다.
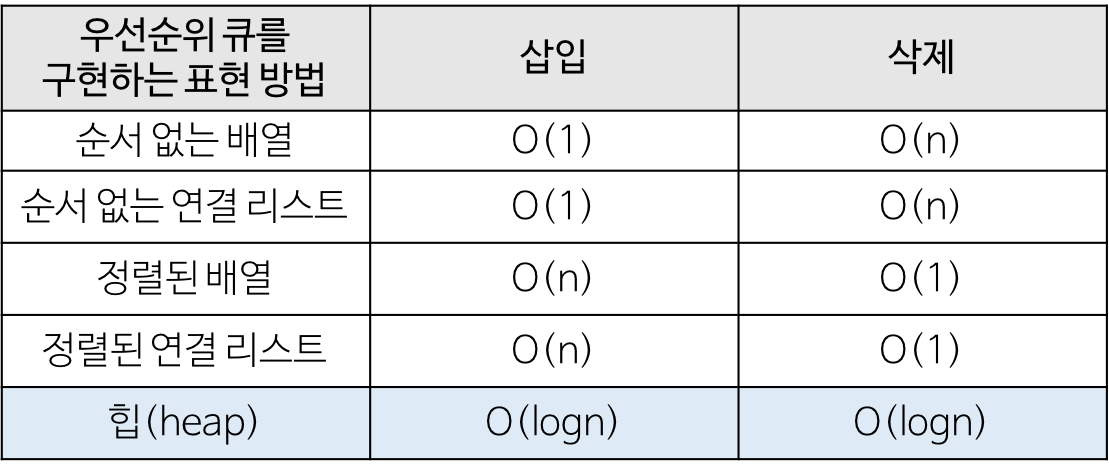
자료구조 Heap(힙)에 대해서
-
완전 이진 트리의 일종이다. 완전 이진트리란, 자식노드의 갯수가 2개 이하이며, 좌측 자식노드는 우즉 자식 노드보다 항상 그 값이 작다. 힙의 완전 이진트리 형태는 느슨한 정렬(반정렬)상태이다. 큰 값일수록 위에 있고, 작은 값일 수록 아래에 있다는 정도의 정렬만 유지하는 형태인 것.(즉 하나의 힙이 있으면, 부모노드가 자식노드보다 항상 값이 큰(혹은 작은) 형태.
-
여러 개의 값들 중, 최대값이나 최소값을 빠르게 찾아내도록 만들어진 자료구조이다.
-
그리고 중복된 값을 허용한다. (원래 이진트리는 중복된 값을 허용하지 않는다.)
-
힙의 종류에 대해서, 최대힙(부모노드가 자식노드보다 항상 크거나 같다) / 최소힙(부모노드가 자식노드보다 항상 작거나 같다), 두종류가있다.
힙의 구현
: 힙을 저장하는 자료구조는 보통 배열을 사용한다.
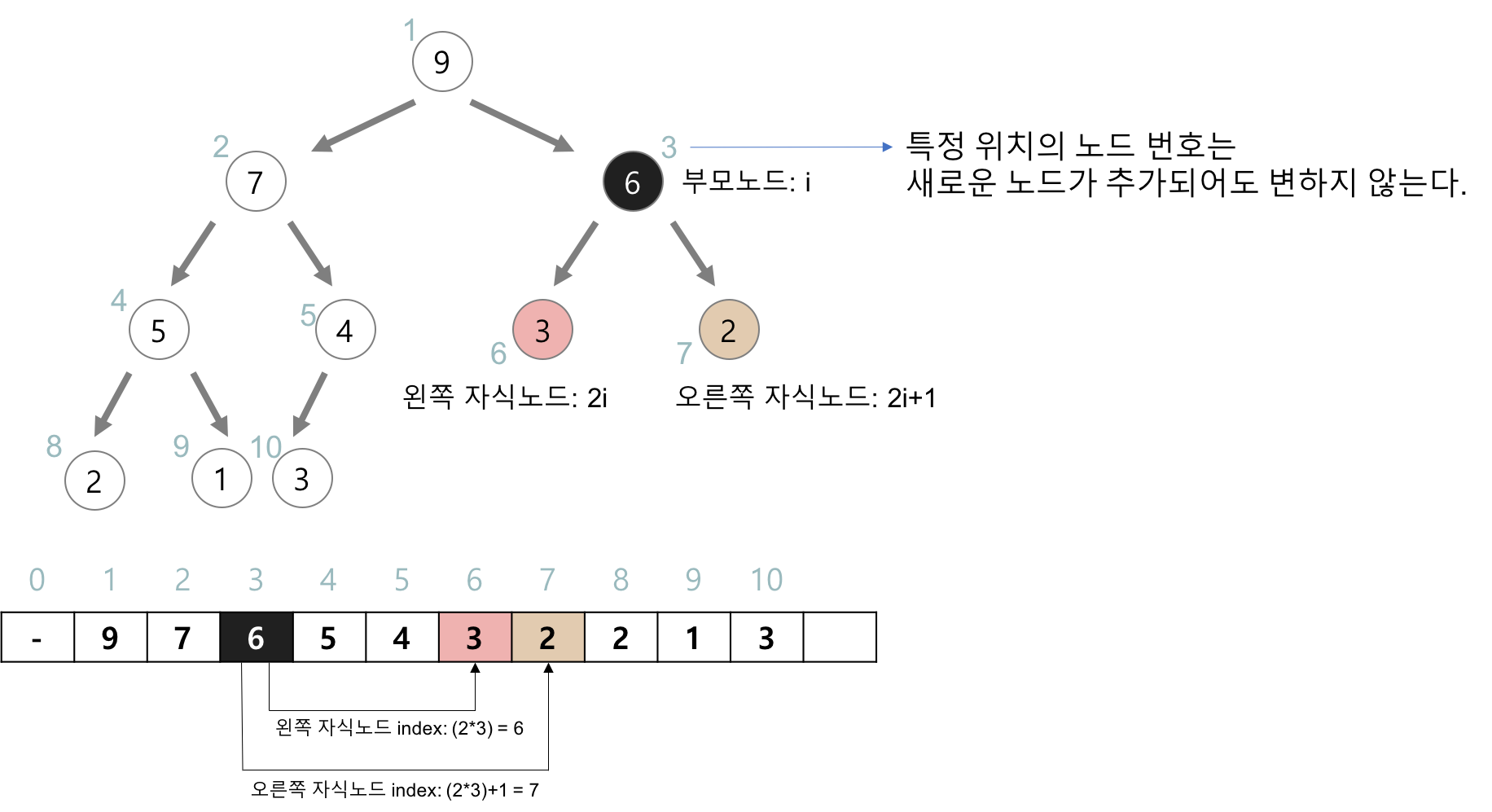
힙에서 부모노드와 자식 노드의 관계
-
임의로 첫번째(root) 노드의 인덱스를 1로 잡고 생각한다. ( 0 은 사용하지 않는다)
-
부모 인덱스 = (자식 인덱스) / 2
-
왼쪽 자식 인덱스 = (부모 인덱스) * 2
-
오른쪽 자식 인덱스 = (부모 인덱스) * 2 + 1
javascript언어를 이용한 heap의 구현
힙 정의
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
function BinaryHeap() {
this._heap = [];
// this compare function will result in a minHeap(최소 힙), use it to make comparisons between nodes in your solution
this._compare = function (i, j) {
return i < j;
};
}
// This function works just fine and shouldn't be modified
BinaryHeap.prototype.getRoot = function () {
return this._heap[0];
};
|
cs |
insert(삽입) 구현
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
//내가 첫번째로 구현한 코드
BinaryHeap.prototype.insert = function (value) {
this._heap.push(value);
//일단 값을 집어넣으 다음에, 크기대로 정리하기
for(let k=0; k<this._heap.length; k++){
for(let i=0; i<this._heap.length-1; i++){
if(this._compare(this._heap[i], this._heap[i+1])=== false){
let change = this._heap[i];
this._heap[i] = this._heap[i+1];
this._heap[i+1] = change;
}
}
}
}
//두번째 방법 while 반복문 활용
BinaryHeap.prototype.insert = function (value) {
this._heap.push(value);
if (this._heap.length === 1) { //힙에 노드가 하나뿐인 경우
return;
}
if (this._heap.length === 2) {
if (this._compare(this._heap[0], this._heap[1])) { //힙에 노드가 두개인 경우
return;
} else {
let temp = this._heap[1];
this._heap[1] = this._heap[0];
this._heap[0] = temp;
return;
}
}
let cur = this._heap.length;
let count = 0
while(count < Math.log(cur) + 1) { //연산을 현재 인덱스의 로그값만큼만 하는 이유는, 힙에서 부모노드 수만큼만 연산한다는 의미이다.
let parent = Math.floor(cur/2);
let temp
if (this._compare( this._heap[parent-1], this._heap[cur-1])) { //실제 연산은 배열에서 일어나므로 힙에서의 인덱스보다 1 작다
return;
}
// 부모 노드가 작지 않다면, (최소 힙 조건에 어긋난다면,) 부모와 자식을 교환한다.
if (!this._compare(this._heap[parent-1], this._heap[cur-1])) {
temp = this._heap[cur-1];
this._heap[cur-1] = this._heap[parent-1];
this._heap[parent-1] = temp;
temp = undefined;
cur = parent; // 부모 자리로 위치가 바뀐 것을 반영해 주고,
}
count++;
}
};
|
cs |
removeRoot 구현
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
|
BinaryHeap.prototype.removeRoot = function () {
let removedRoot = this._heap[0];
// 맨 뒤의 값을 맨 위로 올린 뒤,
this._heap[0] = this._heap.pop();
if (this._heap.length === 1) {
return removedRoot;
}
if (this._heap.length === 2) {
if (this._compare(this._heap[0], this._heap[1])) {
return removedRoot;
} else {
let temp = this._heap[1];
this._heap[1] = this._heap[0];
this._heap[0] = temp;
return removedRoot;
}
}
// heap 안의 값이 3개 이상이면, 본격적으로 탐색함
let count = 0;
//let insertedValueIndex = 0; // root 로 올라간 값의 index (최초에는 root 자리니까 0부터 시작하게 됨.)
let rootIdx = 0
while (count < Math.log(this._heap.length) + 1) {
let leftChildIndex = (rootIdx + 1) * 2 - 1; // 부모 노드의 왼쪽 자식
let rightChildIndex = (rootIdx + 1) * 2; // 부모 노드의 오른쪽 자식
let temp;
// 양쪽 자식하고 다 비교해서 문제 없다면, 그만 돌리고 리턴해라 (기저조건 1)
if (this._compare(this._heap[rootIdx],this._heap[leftChildIndex]) &&
this._compare(this._heap[rootIdx], this._heap[rightChildIndex])
) {
return removedRoot;
}
// 자식 노드가 왼쪽 하나뿐이고, 현재노드가 왼쪽자식보다 작고(더 돌릴 필요 없고,) 오른쪽은 노드가 없다면,
// => 그만 돌리고 리턴해라 (기저조건 2)
if (this._compare(this._heap[rootIdx],this._heap[leftChildIndex]) &&
this._heap[rightChildIndex] === undefined) {
return removedRoot;
}
// 자식 노드가 양쪽 다 없다면,
// => 그만 돌리고 리턴해라 (기저조건 3)
if (this._heap[leftChildIndex] === undefined &&this._heap[rightChildIndex] === undefined) {
return removedRoot;
}
// 위 기저조건을 통과하지 못했다면, 자식 둘 중 하나는 부모보다 작은 것임
// 자식끼리 비교하지 않고 진행하니까, 나중에 이상한 문제가 생김
// 자식끼리 비교해서 더 작은쪽으로 내려가게 해야 할 듯
// 왼쪽 자식이 오른쪽 자식보다 작다면, 부모와 왼쪽 자식을 교환한다.
if (this._compare(this._heap[leftChildIndex], this._heap[rightChildIndex])) {
temp = this._heap[leftChildIndex];
this._heap[leftChildIndex] = this._heap[rootIdx];
this._heap[rootIdx] = temp;
temp = undefined;
rootIdx = leftChildIndex; // 부모 자리로 위치가 바뀐 것을 반영해 주고,
} else {
temp = this._heap[rightChildIndex];
this._heap[rightChildIndex] = this._heap[rootIdx];
this._heap[rootIdx] = temp;
temp = undefined;
rootIdx = rightChildIndex; // 부모 자리로 위치가 바뀐 것을 반영해 주고,
}
count++;
}
return removedRoot;
};
|
cs |
Reference
heap에 대한 개념 : gmlwjd9405.github.io/2018/05/10/data-structure-heap.html
'CS STUDY > Algorithm&Data structure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [JS]알고리즘 문제풀이 12 (0) | 2020.12.09 |
|---|---|
| [JS] 알고리즘 문제풀이 11 (0) | 2020.12.09 |
| [JS]알고리즘 문제풀이 10 (0) | 2020.11.19 |
| [JS]알고리즘 문제풀이 9_재귀활용 (0) | 2020.11.11 |
| [JS]알고리즘 문제풀이 8_linked list활용 (0) | 2020.11.10 |